There are a large variety of Programmers for the AVR's. Among those In-system Programmers are most versatile and easy to use. The Manufacturer Website itself provides different kinds of development kits, Programmers, Debuggers, Emulators, JTAG devices and different addons for the application development using AVR microcontrollers.Also the software tools for programming, simulating the results are also provided. The complete tool set called the AVR studio can be downloaded for free by signing in as a user. The only reason for not using these standard devices(Programmers, debuggers etc. provided by the manufacturers ), is their cost and non availability in certain areas.
This lead to development of new 3rd party programmers which are simple and easy to use. They can just be plugged into one of the ports available on the PC, configured properly with the software can work fine. The best option is to use one of these Programmers. One such is provided at lancos.com. PonyProg is a hex file burner software which works in conjunction with SI-Prog, the ISP, different for different family of Microcontrollers.
PonyProg is a serial device programmer software with a user friendly GUI framework available for Windows95/98/ME/NT/2000/XP and Intel Linux. Its purpose is reading and writing every serial device. At the moment it supports I²C Bus, Microwire, SPI eeprom, the Atmel AVR and Microchip PIC micro.
SI-Prog is the programmer hardware interface for PonyProg.
SI-prog base board remains the same (either DB9 or DB25) while the pins to be connected to the microcontroller changes depending on the series of the microcontroller. These are very well documented in the lancos.com but a first view at them might confuse a newbie.
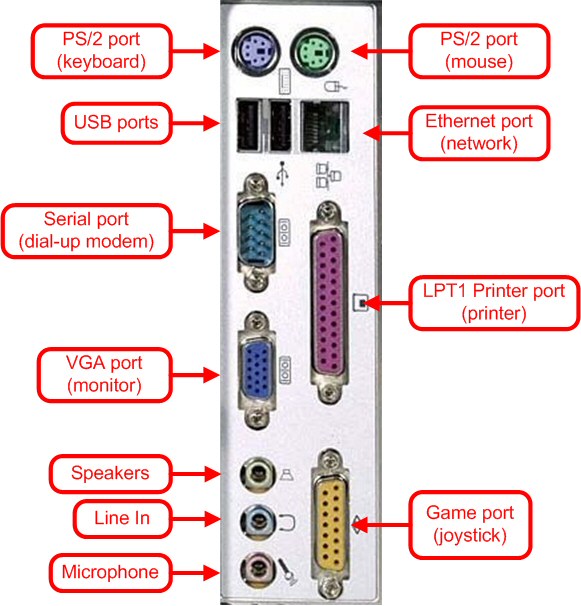
The best option being to make a simple programmer as described in lancos.com. First we have to choose whether to use the PC's parallel port or the serial port. Parallelport or Printerport or LPTport is 25 pin port present in the earlier PC's and in most of the desktops. But in newer PC's these are sometimes omitted. Then your choice must be Serial port or COMport or DB9. Laptops donot have these serial ports and so USB ports are the only left option in such case. Here you can see in detail various PC ports and their Fucntioning.
Parallel Port-view in detail
 Connects a PC to a printer. DOS calls this port LPT1. Another PC XT holdover,
this port is virtually always used to connect to a printer.
Connects a PC to a printer. DOS calls this port LPT1. Another PC XT holdover,
this port is virtually always used to connect to a printer.
A slow but bidirectional 8-bit clocked or unclocked port, this DB-25 port can also be used by scanners, tape drives, and other peripherals.
Serial Port-view in detail
Connect a PC to an external modem, serial mouse, etc. DOS calls these ports COM1-COM4. The small version is slightly more popular than the large version. Dating from the PC XT, these are ubiquitous but rarely used.
Both the small (male DB-9) and large (male DB-25) versions are electrically identical, and can be interchanged with a simple adapter.They both speak RS-232, a relatively slow (around 105Kbps max) and error-prone protocol. The default controller is CPU-intensive and low data rate. A better UART, common on modern machines, is the 16550A, which has a 1KB buffer.
This lead to development of new 3rd party programmers which are simple and easy to use. They can just be plugged into one of the ports available on the PC, configured properly with the software can work fine. The best option is to use one of these Programmers. One such is provided at lancos.com. PonyProg is a hex file burner software which works in conjunction with SI-Prog, the ISP, different for different family of Microcontrollers.
PonyProg is a serial device programmer software with a user friendly GUI framework available for Windows95/98/ME/NT/2000/XP and Intel Linux. Its purpose is reading and writing every serial device. At the moment it supports I²C Bus, Microwire, SPI eeprom, the Atmel AVR and Microchip PIC micro.
SI-Prog is the programmer hardware interface for PonyProg.
SI-prog base board remains the same (either DB9 or DB25) while the pins to be connected to the microcontroller changes depending on the series of the microcontroller. These are very well documented in the lancos.com but a first view at them might confuse a newbie.
The best option being to make a simple programmer as described in lancos.com. First we have to choose whether to use the PC's parallel port or the serial port. Parallelport or Printerport or LPTport is 25 pin port present in the earlier PC's and in most of the desktops. But in newer PC's these are sometimes omitted. Then your choice must be Serial port or COMport or DB9. Laptops donot have these serial ports and so USB ports are the only left option in such case. Here you can see in detail various PC ports and their Fucntioning.
Parallel Port-view in detail
 Connects a PC to a printer. DOS calls this port LPT1. Another PC XT holdover,
this port is virtually always used to connect to a printer.
Connects a PC to a printer. DOS calls this port LPT1. Another PC XT holdover,
this port is virtually always used to connect to a printer.A slow but bidirectional 8-bit clocked or unclocked port, this DB-25 port can also be used by scanners, tape drives, and other peripherals.
Serial Port-view in detail
Connect a PC to an external modem, serial mouse, etc. DOS calls these ports COM1-COM4. The small version is slightly more popular than the large version. Dating from the PC XT, these are ubiquitous but rarely used.
Both the small (male DB-9) and large (male DB-25) versions are electrically identical, and can be interchanged with a simple adapter.They both speak RS-232, a relatively slow (around 105Kbps max) and error-prone protocol. The default controller is CPU-intensive and low data rate. A better UART, common on modern machines, is the 16550A, which has a 1KB buffer.


No comments:
Post a Comment